Habitat & Blooms
Habitat
Most jellyfish are marine animals, although a few hydromedusae inhabit freshwater. The best known freshwater example is the cosmopolitan hydrozoan jellyfish, Craspedacusta sowerbii. It is less than an inch (2.5 cm) in diameter, colorless and does not sting. Some jellyfish populations have become restricted to coastal saltwater lakes, such as Jellyfish Lake in Palau. Jellyfish Lake is a marine lake where millions of golden jellyfish (Mastigias spp.) migrate horizontally across the lake daily.
Although most jellyfish live well off the ocean floor and form part of the plankton, a few species are closely associated with the bottom for much of their lives and can be considered benthic. The upside-down jellyfish in the genus Cassiopea typically lie on the bottom of shallow lagoons where they sometimes pulsate gently with their umbrella top facing down. Even some deep-sea species of hydromedusae and scyphomedusae are usually collected on or near the bottom. All of the stauromedusae are found attached to either seaweed or rocky or other firm material on the bottom.
Some species explicitly adapt to tidal flux. In Roscoe Bay, jellyfish ride the current at ebb tide until they hit a gravel bar, and then descend below the current. They remain in still waters until the tide rises, ascending and allowing it to sweep them back into the bay. They also actively avoid fresh water from mountain snowmelt, diving until they find enough salt.
Blooms
Jellyfish form large masses or blooms in certain environmental conditions of ocean currents, nutrients, sunshine, temperature, season, prey availability, reduced predation and oxygen concentration. Currents collect jellyfish together, especially in years with unusually high populations. Jellyfish can detect marine currents and swim against the current to congregate in blooms. Jellyfish are better able to survive in nutrient-rich, oxygen-poor water than competitors, and thus can feast on plankton without competition. Jellyfish may also benefit from saltier waters, as saltier waters contain more iodine, which is necessary for polyps to turn into jellyfish. Rising sea temperatures caused by climate change may also contribute to jellyfish blooms, because many species of jellyfish are able to survive in warmer waters. Increased nutrients from agricultural or urban runoff with nutrients including nitrogen and phosphorus compounds increase the growth of phytoplankton, causing eutrophication and algal blooms. When the phytoplankton die, they may create dead zones, so called because they are ahypoxic (low in oxygen). This in turn kills fish and other animals, but not jellyfish, allowing them to bloom. Jellyfish populations may be expanding globally as a result of land runoff and overfishing of their natural predators. Jellyfish are well placed to benefit from disturbance of marine ecosystems. They reproduce rapidly; they prey upon many species, while few species prey on them; and they feed via touch rather than visually, so they can feed effectively at night and in turbid waters. It may be difficult for fish stocks to reestablish themselves in marine ecosystems once they have become dominated by jellyfish, because jellyfish feed on plankton, which includes fish eggs and larvae.
Some jellyfish populations that have shown clear increases in the past few decades are invasive species, newly arrived from other habitats: examples include the Black Sea, Caspian Sea, Baltic Sea, central and eastern Mediterranean, Hawaii, and tropical and subtropical parts of the West Atlantic (including the Caribbean, Gulf of Mexico and Brazil).
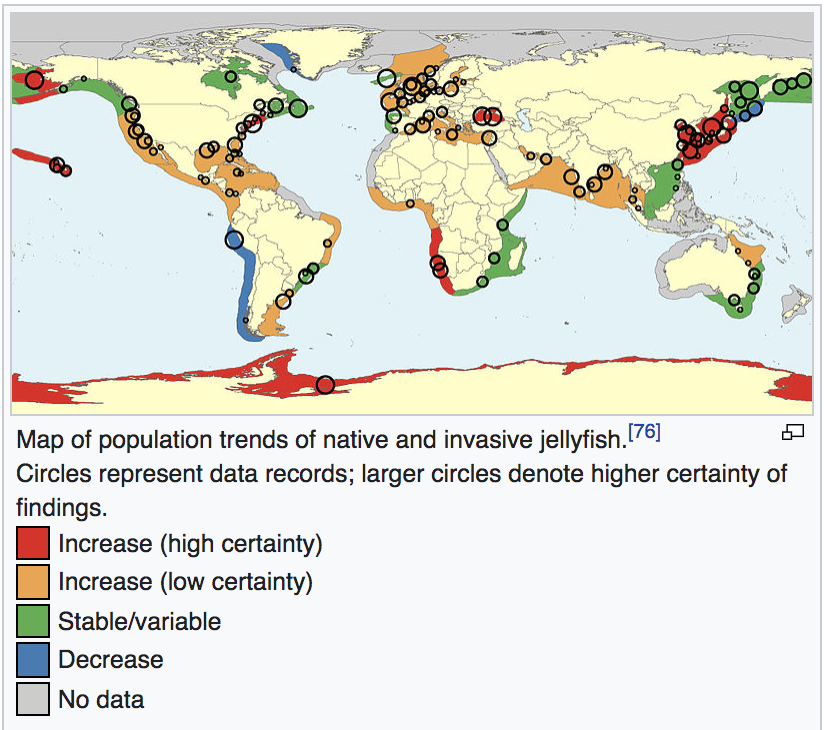
.png)
Jellyfish blooms can have significant impact on community structure. Some carnivorous jellyfish species prey on zooplankton while others graze on primary producers. Reductions in zooplankton and icthyplankton due to a jellyfish bloom can ripple through the trophic levels. High density jellyfish populations can out compete other predators and reduce fish recruitment. Increased grazing on primary producers by jellyfish can also interrupt energy transfer to higher trophic levels.
During blooms, jellyfish significantly alter the nutrient availability in their environment. Blooms require large amounts of available organic nutrients in the water column to grow, limiting availability for other organisms. Some jellyfish have a symbiotic relationship with single-celled dinoflagellates, allowing them to assimilate inorganic carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen creating competition for phytoplankton.[97] Their large biomass makes them an important source of dissolved and particulate organic matter for microbial communities through excretion, mucus production, and decomposition. The microbes break down the organic matter into inorganic ammonium and phosphate. However, the low carbon availability shifts the process from production to respiration creating low oxygen areas making the dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphorus largely unavailable for primary production.
These blooms have very real impacts on industries. Jellyfish can out compete fish by utilizing open niches in over-fished fisheries. Catch of jellyfish can strain fishing gear and lead to expenses relating to damaged gear. Power plants have been shut down due to jellyfish blocking the flow of cooling water. Blooms have also been harmful for tourism, causing a rise in stings and sometimes the closure of beaches.